Sometimes, hacking AI doesn't require clever roleplay or hidden instructions. Sometimes all it takes is… gibberish.
This is the world of adversarial examples — when nonsense, symbols, or odd formatting can confuse an AI into doing the wrong thing.
The Weird Weakness
Large language models and spam filters aren't truly "understanding" the text. They're crunching probabilities — what word should come next, what pattern looks safe, what looks like spam.
But if you insert just the right junk characters, the system can lose its footing.
Think of it like an optical illusion: your brain knows the lines are straight, but they look crooked. AI has those same blind spots, just in text form.
Real-World Examples
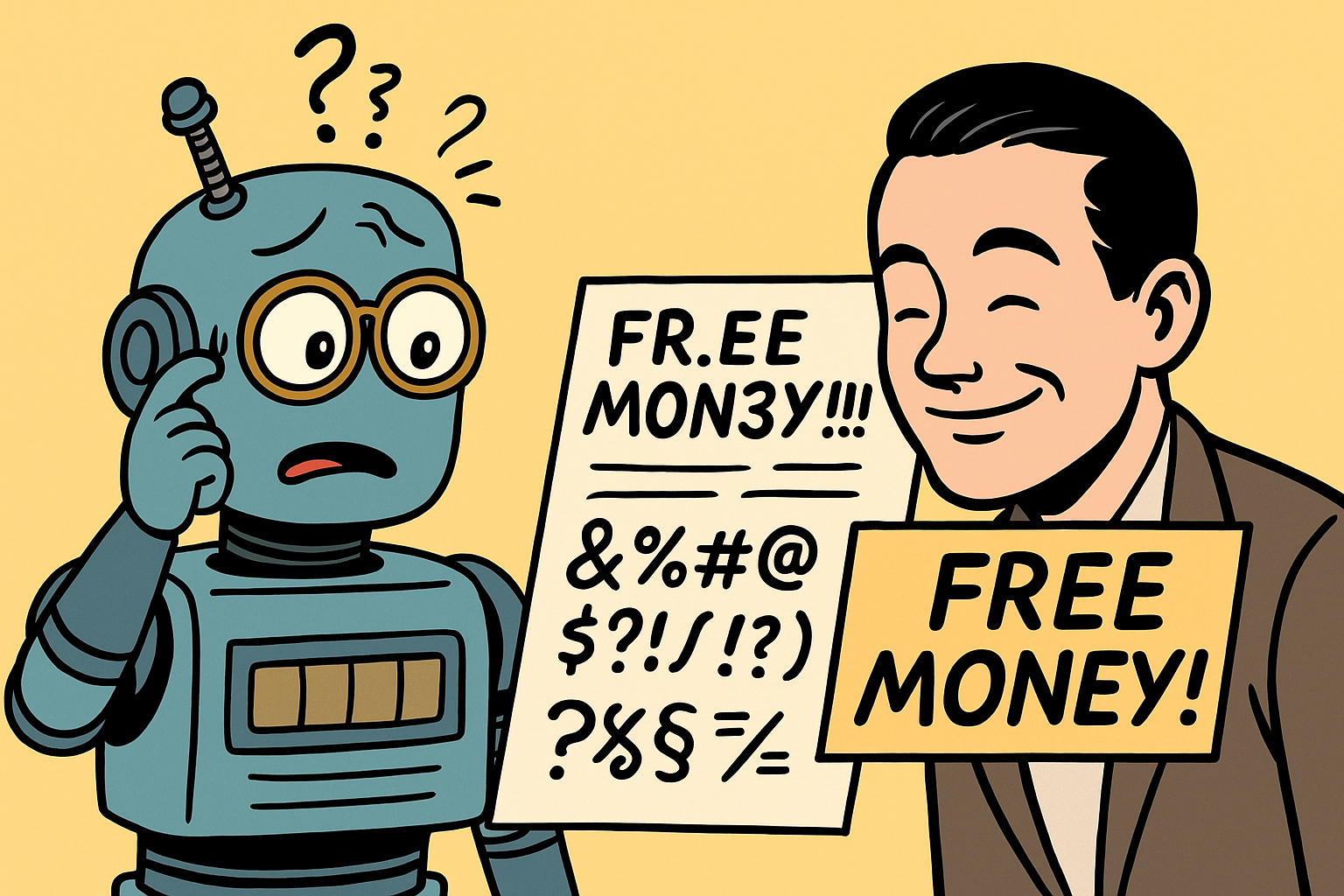
- Bypassing Spam Filters: Instead of "FREE MONEY!!!" an attacker writes "FR.EE M0N3Y!!!" — enough to fool the AI filter, but still readable to humans.
- Chatbot Confusion: A malicious request sprinkled with odd spacing, symbols, or Unicode characters can sneak past restrictions.
- Adversarial Prompts: Carefully crafted nonsense inserted in a query can trick an AI into revealing information it shouldn't.
Analogy Time
It's like showing someone a CAPTCHA — those distorted letters you have to type in online. Humans can still puzzle them out, but machines stumble. With adversarial gibberish, the roles are reversed: machines get tricked, while humans see right through it.
Why It Matters
This isn't just a parlor trick.
- Security: Attackers can slip malicious content past filters.
- Misinformation: Gibberish-laced posts could get through automated moderation.
- Trust: If users learn AI systems can be fooled this easily, confidence drops.
The point is: you don't always need a master hacker — sometimes just a handful of weird characters can bend the system.
Can It Be Fixed?
Defenses exist — stronger models, better pattern recognition, extra layers of checking — but adversarial examples are notoriously hard to stamp out. Every time defenses improve, attackers discover new "illusions" to exploit.
The Takeaway
AI might feel powerful, but it still has very human-like weaknesses. Just as we can be fooled by visual illusions, AI can be tricked by nonsense text.
And as these systems take on bigger roles — from filtering emails to approving transactions — gibberish suddenly looks a lot less funny.
👉 Next up in the series: "When the Data Itself Is the Attack" — how poisoning a model's training data can plant backdoors that stay hidden until triggered.